Diabetes affects one out of every ten persons worldwide. India has 72.9 million adults affected by this silent epidemic, making it the country with the second most diabetes patients. With almost 116 million diabetics, China tops the list. If you have diabetes, your body is unable to properly digest and utilise glucose obtained from your diet. There are different types of diabetes, each with its own set of causes, but they all have one thing in common: too much glucose in the bloodstream. Type 2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed, hence it is important to raise awareness about this disease and find ways to reduce your risk.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes develops when your body’s cells are unable to absorb sugar (glucose) and utilise it for energy. Extra sugar builds up in your system as a result of this. Diabetes that is not well controlled can have serious health complications, including damage to a variety of organs and tissues in your body, including your heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves. The different types of diabetes include:
- Type 1 diabetes
This condition is an autoimmune disease, meaning your body attacks itself. The insulin-producing cells in your pancreas are damaged in this situation. Type 1 diabetes affects up to 10% of patients with diabetes. It is most commonly diagnosed in children and young people, and it is also known as “juvenile” diabetes. People with Type 1 diabetes must take insulin on a daily basis. - Type 2 diabetes
With this type, your body either doesn’t make enough insulin or your body’s cells don’t respond normally to the insulin. It is the most common type of diabetes and up to 95% of people with diabetes have Type 2. - Prediabetes
This type is the stage before Type 2 diabetes. Your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be officially diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes. - Gestational diabetes
This type develops in some women during their pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after pregnancy. However, for some women it may increase your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later on in life.
Symptoms of Diabetes
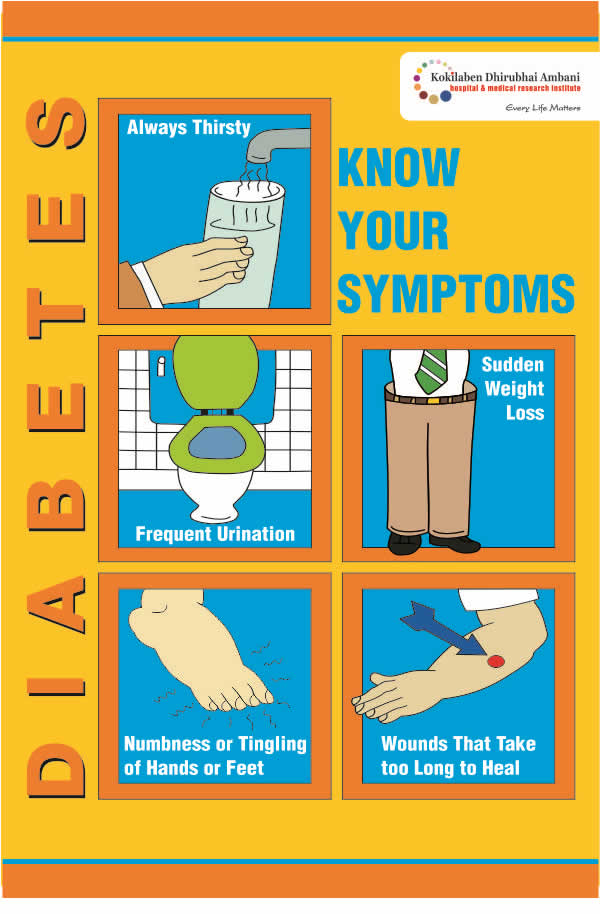
Type 2 diabetes symptoms often appear gradually over several years and are so minor that you may not even notice them. The following are the most prevalent symptoms of type 2 diabetes that should be investigated further:
- Frequent urination
- Feeling very thirst and hungry
- Unexplained weight loss
- Having a blurry vision
- Numbness or tingling of hands or feet
- Feel very tired
- Slow healing wounds
Risk factors for Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is known to have a substantial hereditary component, meaning it runs in families. Your chances of getting this disease increase considerably if you have a parent, brother, or sister who has it. Apart from your family history, the below factors highly increase your risk of getting type 2 diabetes:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Prediabetes
- Unhealthy food habits
- High alcohol intake
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Being obese or overweight
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Diabetes complications
Diabetics are at a higher risk of having a variety of major health conditions. High blood glucose levels over time can lead to significant disorders of the heart and blood vessels, as well as the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and teeth. In addition, people with diabetes are more likely to contract infections. Diabetes is a leading cause of cardiovascular illness, blindness, kidney failure, and lower limb amputation too. Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly to help delay or prevent diabetic complications. Here are the most common health complications seen in diabetics:
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Cardiovascular disease
- Diabetic nephropathy
- Pregnancy complications
- Diabetic foot disease
Preventive Diabetes care
You may be able to avoid or delay the onset of diabetes if you are at risk. Making healthy lifestyle changes on time will help reduce your risk of getting type 2 diabetes. Here are some of the recommended preventive measures:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Follow a healthy diet plan
- Exercise regularly
- Quit smoking
- Monitor your health numbers
- Know your risk
Diabetes care at Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital
Diabetes is a chronic disease that can lead to serious complications if not treated effectively by a specialist. Consult highly trained and experienced doctors at our Centre for Diabetes and Bariatric Surgery for a multidisciplinary approach. Our team helps you learn everything you need to know about diabetes prevention, care, treatment, and management. From diagnosis to diet plan to obesity management our doctors look into everything. Although there is currently no treatment for diabetes, regulating your blood sugar levels can help you live a healthier life. Early diagnosis and treatment is the best way to reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related complications. Please find below our website details for further information: https://www.kokilabenhospital.com/departments/centresofexcellence/centrefor_diabetesbariatricsurgery.html