Blood donation happens when a person voluntarily agrees for his or her blood to be extracted and donated to a person in need. It is a noble deed that helps humanity. Donated blood can be used for an emergency transfusion or can be separated into individual components to be used later. Donating Blood is a safe and easy process and helps save many lives.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), India suffers from an annual deficit of two million blood units, as only 1% of the Indian population donates blood each year. India faced a shortage of 1.95 million units of blood in 2019.
Who needs Blood Transfusions?
Blood transfusions are a critical part of everyday medicine. A person may need a blood transfusion for a variety of reasons. The most common situations include:
- Surgeries
- Accidents and Trauma
- Childbirth complications
- Organ Transplant
- Cancer therapies
- Thalassemia patients
- Sickle cell anaemia patients
Blood Donation Process
The complete blood donation process which includes all the registration and formalities takes about an hour. The donation itself is only about 15 minutes. Here is the blood donation process:
- If you’re donating whole blood, the area on your arm is cleansed and a sterile needle is used to extract blood.
- The blood donor is seated comfortably or lying down.
- Once the blood donation is complete a bandage is placed on your arm.
- Platelet donation is slightly different from giving a whole-blood donation.
During the platelet donation, blood is removed from one arm, and then a centrifuge separates out the platelets. The rest of the blood then returns to the donor through the other arm.
Who can Donate Blood?
Most people can give blood if they are in good health.
What makes you Eligible:
- Any donor, who is healthy, fit and not suffering from any transmittable diseases can donate blood.
- The Donor must be 18 -60 years age and should weigh minimum 50 kgs.
- The Donor’s Haemoglobin level must be 12.5g/dl minimum.
- A donor can again donate blood after 3 months of the last donation.
- Pulse rate must be between 50 to 100mm without any irregularities.
- Blood Pressure Diastolic 50 to 100 mm Hg and Systolic 100 to 180 mm Hg.
- Body temperature should be normal.
What makes you Non-Eligible:
- Patients of cardiac arrest, hypertension, kidney disease or epilepsy.
- Consumption of alcohol within the last 24 hours.
- HIV + status
- Having a cold, flu, sore throat, or any other infection.
- Pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers cannot donate blood.
Myths and Facts
Every year there is a shortage in the actual demand and supply of Blood donations across India. There are many misconceptions regarding blood donations that must be cleared. Here are a few myths and facts about blood donation:
Myth #1: Giving blood hurts.
Fact: The only pain you’ll feel is the quick prick of the needle when it is inserted. The area may be slightly sore afterward, but this settles in a few hours.
Myth #2: Blood donation increases the risk of infections.
Fact: A new sterile needle is used each time someone donates blood and is then immediately discarded. Strict procedures are followed to avoid any kind of infection.
Myth #3: I can’t give blood because I have high cholesterol.
Fact: Having high cholesterol does not disqualify you from donating blood, as long as you are otherwise healthy. Consult your doctor for more details.
Myth #4: I can’t give blood because I am on medication.
Fact: As long as you are healthy, most medications will not disqualify you from donating blood. Speak to your doctor to clear your doubts about this.
Myth #5: Blood donation takes a lot of time.
Fact: The whole procedure of blood donation from the time of registration takes less than 1 hour.
Myth #6: Blood donation lowers your immunity.
Fact: This is completely false. Your body’s immunity level is not affected by blood donation.
Myth #7: Donating blood frequently causes an iron deficiency.
Fact: No, a healthy individual with good eating habits can donate blood four times a year with a gap of three months. It does not affect your iron levels.
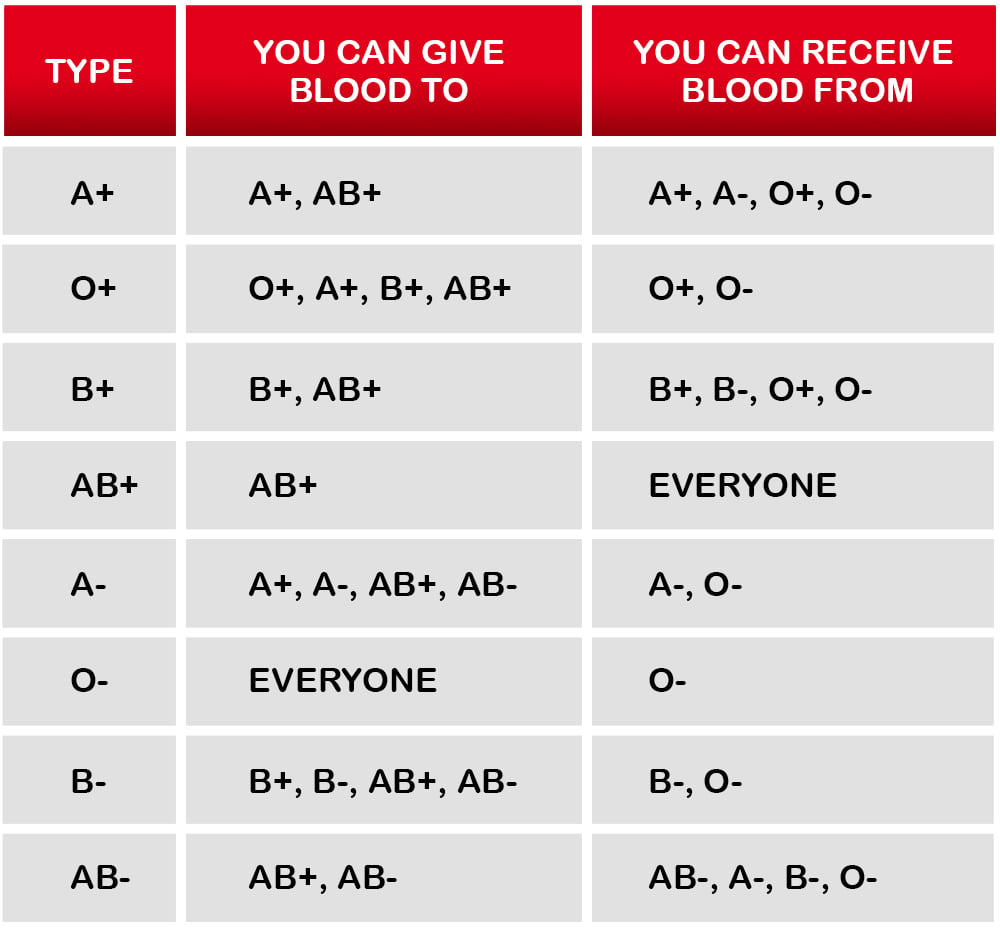
Blood Group Types
There are eight different blood types, and they’re not always compatible with each other. People who have O-negative blood are considered universal donors for the entire population. Here are the further details for quick reference:
Blood Donation and COVID-19
Does COVID-19 spread through blood donations?
No, this is a reparatory illness and does not spread by blood transfusion.
Anyone who is not showing any symptoms of COVID-19 currently or has not come in contact with a patient of COVID 19, can donate blood. The fear of the current pandemic and the lockdown has seen a reduction in the number of blood donors. It has caused an unprecedented shortage of blood in the blood bank. There is no substitute for blood. Donate blood, help save lives.
Take these precautions when you go for Blood Donation:
- Take an appointment to avoid crowds.
- Wear a mask.
- Carry a hand sanitizer and use it frequently.
- Maintain social distancing while at the hospital.
The Blood Bank at Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art equipment, and use advanced techniques for processing and screening of blood and its components. We follow a stringent check on all samples before blood transfusion. Donating blood now is more important than ever before. Call our Blood Bank on 022-30937293 to donate blood. Please find below link for further details:


