Childhood obesity is on the rise. Childhood obesity is not just a cosmetic problem anymore as these children are likely to stay obese into adulthood and more likely to develop diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular disorders at a younger age.
Causes

- Increased intake of junk and processed food products that are high in fat and sugars but low in vitamins, minerals and other healthy micronutrients
- Decreased physical activity levels with the growing use of computers, increased time watching television and decreased physical education in schools
- Heredity and family history of obesity
- Social and economic development and policies in the areas of agriculture, transport, urban planning, food processing, distribution and marketing
Consequences
A higher chance of premature death or disability in adulthood Obesity into adulthood associated with many short-term and long-term health problems Developing Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) like diabetes and cardiovascular disorders at a younger age
Prevention
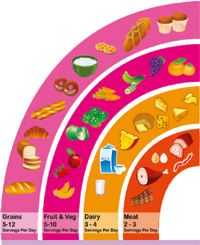
- By including more fruits and vegetables as well as legumes, whole grains and nuts in your diet
- By limiting energy intake of total fats, and shifting fat consumption from saturated fats to unsaturated fats
- By restricting the intake of sugars and salt rich foods
- By increasing physically activity, i.e., at least 60 minutes of regular, moderate to vigorous-intensity activity everyday
Just Remember
- Always start a meal with salads
- Minimise the use of high-calorie dressings, cheese, butter, mayo and sauces
- Choose grilled rather than fried foods, thus avoiding items like French fries, fried snacks and deep-fried chicken
- Select low-fat milk or orange juice rather than high-fat milk shakes
- Avoid purchasing salt-rich foods like
- processed cheese, fast foods, ready-to-eat food products, salad dressings, pickles and potato chips
- Limit the intake of beverages, such as
- carbonated soft drinks and carton juices
- Practice balance, variety and moderation in your as well as your family’s diet, and your children are likely to follow suit